
Small cap growth stocks have been trading at a big valuation discount to their large cap growth peers for some time, but the gap started to narrow after the July 11 CPI print raised the prospect of rate cuts. Are you positioned for a potential rotation?
After the release of June’s weaker-than-expected inflation numbers (CPI fell 0.1%),1 the potential for Fed rate cuts grew more likely—and small cap stocks reacted positively. Investors rotated toward cyclical, interest rate sensitive small cap growth names, and small cap growth outperformed large cap growth by over 500 basis points in just one day.2
Is this the rotation we’ve been waiting for? We can’t know for sure, but we’ve been anticipating this move for some time. And when small caps move, they move fast!
Time may still be on your side, however, because small cap stocks continue to look cheap, relatively speaking:
- Small cap growth ended June at a 37% valuation discount to large cap growth.3
- The Russell 2000 Growth Index is trading 17% below its high-water mark of 1726 set in February 2021 (see chart), while large cap indexes are near record highs.
As we’ve said for several quarters, we believe the setup for small cap growth stocks is compelling—but you need a small cap allocation before you can participate in any potential upside. Take a look at your portfolio. Will you be well-positioned if the market continues to rotate to small cap stocks?
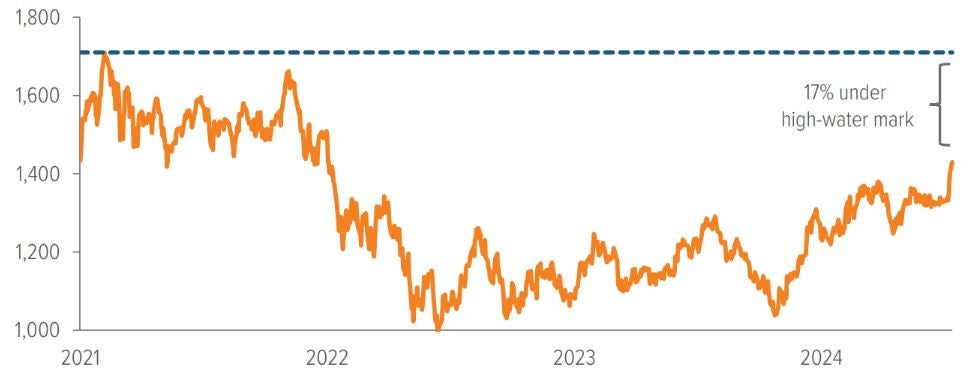
As of 07/15/24. Source: FactSet. Chart shows closing prices. Feb. 2021 high of 1726 was intra-day high. See index information at the end of this document.
A note about riskThe principal risks are generally those attributable to investing in stocks and related derivative instruments. Holdings are subject to market, issuer and other risks, and their values may fluctuate. Market risk is the risk that securities or other instruments may decline in value due to factors affecting the securities markets or particular industries. Issuer risk is the risk that the value of a security or instrument may decline for reasons specific to the issuer, such as changes in its financial condition. More particularly, the strategy invests in smaller companies which may be more susceptible to price swings than larger companies because they have fewer resources and more limited products, and many are dependent on a few key managers. |

